Bone Augmentation
Advanced techniques enhance bone structure for successful dental implant placement. Bone augmentation procedures improve implant stability and success rates.
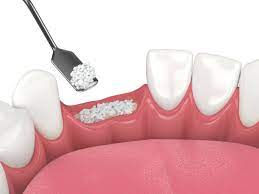
Bone Grafting
Bone grafting is a frequently performed procedure in dentistry, particularly in the context of dental implants. This procedure becomes necessary when an individual loses a tooth or experiences significant bone loss in the jaw, often due to factors such as gum disease or injury. In situations where there is insufficient healthy bone to support a dental implant, bone grafting is employed to augment the jawbone. This process aims to create a solid and supportive foundation for the successful placement of a dental implant.
When is Bone Grafting Necessary?
Bone grafting becomes necessary under the following circumstances:
1. Insufficient Bone Volume:
- When the jawbone lacks the required thickness and height to adequately support dental implants, bone grafting is necessary to augment the bone structure.
2. Tooth Loss and Bone Resorption:
- Following tooth loss, the jawbone may undergo resorption or shrinkage due to the absence of stimulation. In such cases, bone grafting becomes essential to ensure the success of dental implant placement.
Bone Grafting Procedure
The bone grafting procedure is a carefully orchestrated series of steps to prepare and place graft material into the targeted area of the jawbone. This process allows the grafted bone to integrate with the existing bone, creating a strong foundation for dental implants.
Step 1: Pre-Operative Assessment
Before the bone grafting procedure, the dentist conducts a comprehensive pre-operative assessment of the patient's oral health. This assessment includes X-rays and 3D imaging to determine the extent of bone loss and identify the most suitable grafting material.
Step 2: Harvesting the Graft Material
For autografts, the dentist harvests bone from another area of the patient's body, such as the jaw or hip. The donor area is numbed with local anaesthesia to ensure a comfortable experience.
Step 3: Graft Placement
Once the graft material is prepared, the dentist carefully places it into the targeted area of the jawbone where the dental implant will be inserted. The graft material acts as a scaffold for new bone growth.
Step 4: Healing and Integration
Over the next few months, the grafted bone integrates with the existing jawbone through a process known as osseointegration. During this healing period, patients must follow the dentist's instructions for proper oral hygiene and care.
Step 5: Dental Implant Placement
After the successful fusion of the graft with the jawbone, the dental implant procedure can proceed. A small titanium post, known as the dental implant, is inserted into the grafted area, serving as the artificial tooth root.
Step 6: Crown Placement
Once the implant fully integrates with the jawbone, an abutment and crown are attached to the implant, completing the dental restoration. The crown is designed to match the surrounding natural teeth, providing a natural-looking and functional result.